Types of Hearing Loss |
|
Conductive Hearing Loss |
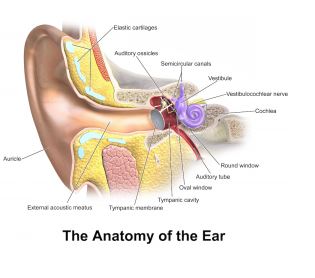 |
| This type of hearing loss results from problems in the middle or outer ear. It may be treated medically through the use of medication or surgery. Causes of conductive hearing loss include ear infections, congenital anomalies, blockage in the ear canal, holes in the eardrum, or injury to the outer ear. |
|
Sensorineural Hearing Loss |
|
| This type of hearing loss results from a problem in the inner ear, auditory nerve, or brain. It is usually permanent and can be treated using hearing aids, or cochlear implants. Common causes include heredity, infections, serious illnesses, noise exposure, trauma, or medications. | |
Mixed Hearing Loss |
|
| This type of hearing loss results from a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. | |
When you suspect a hearing loss |
|
| If a hearing loss is suspected in a child, parents or caregivers should schedule an evaluation with an Audiologist with both the experience and equipment necessary to test children. Even if the child passes a newborn hearing screening or previous hearing tests, they should be rechecked periodically. Current screening methods are good at detecting moderate to profound hearing losses, but may fail to detect mild hearing loss. | |
Hearing Loss Prevention in Children |
|
| There are some things parents can do to reduce the risk of hearing loss with their children. These include: | |
|
|
